Difference between revisions of "User Record Import Guide"
From Adjutant Wiki
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
==User Record Import Notes== | ==User Record Import Notes== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Import User screen creates the User in Adjutant attribute record, links it to the Contact ID, and can complete all of the required fields in the User Details tab and the User Password Settings tab. The import program can even establish user security mimics. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
===Timing and Preparation=== | ===Timing and Preparation=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | User in Adjutant details and all of the appropriate named user license flags should be set up as soon as possible once the core system setup items have been completed. User licenses are generally billed from the very beginning of the implementation, so customers should be able to access the system as soon as it is available. Setting up user records immediately avoids a situation where customers are being billed for user licenses that they are unable to use. | ||
All Address Book setup items should be completed prior to beginning the Contacts, Customer, and Vendor imports. The [[Address Book Setup Guide]] covers all of the Rule Maintenance records that should be completed prior to importing customer, vendor and contact records. | All Address Book setup items should be completed prior to beginning the Contacts, Customer, and Vendor imports. The [[Address Book Setup Guide]] covers all of the Rule Maintenance records that should be completed prior to importing customer, vendor and contact records. | ||
| − | + | The User Import can be completed immediately after the employee contact records have been imported with the Import Contacts screen, or after they have been added manually. The internal contact records should be added prior to completing the Customer and Vendor imports. User records, resource records, salespersons, account managers, buyers, and project attributes should be established for employee records prior to importing the Organization records so that links to salespersons, account managers, and buyers can be made in the organization import files. | |
| − | |||
| Line 37: | Line 42: | ||
| − | == | + | ==User Record Import File Data Scrubbing== |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Since nearly all of the data fields in the User Import file are Adjutant security specific fields, the customer will not have a source file to provide for this data. Generally, the only customer-supplied data for this file will be the userids, passwords, and email settings. In many cases the userids and passwords will be generated by ABIS personnel. | |
| − | + | Because the data for this file is mostly generated by ABIS personnel to speed up the process of adding users, there is no customer data scrubbing required. | |
Revision as of 07:23, 17 October 2018
Contents
General Import Template File Notes
- Template files are typically generated from their respective Import screen using an 'Export Template' button.
- Using the 'Export Template' button from an updated system will help ensure that you provide the customer with the most up-to-date import file, and will help avoid errors.
- Templates generally (but not in all cases) contain 3 rows of header information.
- The first row is generally labelled with f1 through f## and is used to give a consistent column id to each data column. Do not remove this row unless instructed.
- The second row is labelled with the column data/field name. The values in this row are used for the file mapping screen. Editing these values is generally not needed and may make the mapping process difficult.
- The third row is labelled with the same values from row 2, an is available to create a customer-friendly name for the associated data column.
- The third row should be removed from the source file prior to importing. It will cause errors since it will be treated as the first import record on the file.
- Import files MUST always be saved as 'Microsoft Excel 5.0/95 Workbook (*.xls)' format (until further notice). The import screens will generate errors if the file type is not correct.
- It is a good idea to perform a Mapping Table Import using a current source list before beginning on any imports. Without a current mapping table, the quality of imports can be compromised.
- Export a current list from a good source (such as ABIS)
- Perform a Mapping Table Import on the target system with the XLS file from the step above
User Record Import Notes
The Import User screen creates the User in Adjutant attribute record, links it to the Contact ID, and can complete all of the required fields in the User Details tab and the User Password Settings tab. The import program can even establish user security mimics.
Timing and Preparation
User in Adjutant details and all of the appropriate named user license flags should be set up as soon as possible once the core system setup items have been completed. User licenses are generally billed from the very beginning of the implementation, so customers should be able to access the system as soon as it is available. Setting up user records immediately avoids a situation where customers are being billed for user licenses that they are unable to use.
All Address Book setup items should be completed prior to beginning the Contacts, Customer, and Vendor imports. The Address Book Setup Guide covers all of the Rule Maintenance records that should be completed prior to importing customer, vendor and contact records.
The User Import can be completed immediately after the employee contact records have been imported with the Import Contacts screen, or after they have been added manually. The internal contact records should be added prior to completing the Customer and Vendor imports. User records, resource records, salespersons, account managers, buyers, and project attributes should be established for employee records prior to importing the Organization records so that links to salespersons, account managers, and buyers can be made in the organization import files.
General Notes
Phone Numbers - It is best practice to follow a set pattern for the 4 phone number codes that can be imported. Using the codes from the Contact Phone Codes (PHONECODES) rule, establish a consistent pattern for coding all imported phone number. For example, all Phone1 Codes should be Cell(CE), all Phone2 codes should be Home(HO), and so on. Ideally, the order of the phone codes should match the order set in the rule.
Contact Attributes - The contact import process can attach all of the required contact attributes during the import process. However, it is important to know that each attribute selected during the import process will be applied to ALL contacts imported on that import process. The contact import file may need to be split into several separate import files, and run in batches, if unique attributes are needed for certain groups of contacts.
Address Data - Addresses will not automatically pull from the associated Custno. The AddressA (Business) details must exist in the import file in order to get created with the contact record.
User Record Import File Data Scrubbing
Since nearly all of the data fields in the User Import file are Adjutant security specific fields, the customer will not have a source file to provide for this data. Generally, the only customer-supplied data for this file will be the userids, passwords, and email settings. In many cases the userids and passwords will be generated by ABIS personnel.
Because the data for this file is mostly generated by ABIS personnel to speed up the process of adding users, there is no customer data scrubbing required.
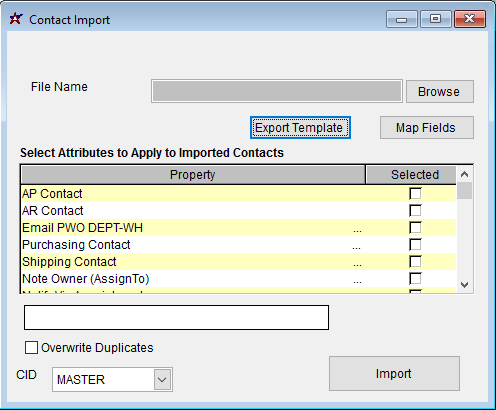
Contact Import Screen (IMPORTCONTACT)
Menu Location: Transaction>>Importers/Exporters>>Address Book>>Contact Import
File Name/Browse: Use the Browse button to locate and select the completed contact import template file (in XLS format)
Export Template: Generates a blank Contact Import template file
Map Fields: Fields must be mapped prior to importing. If no changes have been made to the column headings, the mapping screen should show all green, and you can click OK to continue. If any of the Input Field Name columns on the left are red, single-click on the line on the left column, and then double-click the desired mapped field in the right column to complete the mapping. Repeat for any red lines on the left that should be mapped. If there are additional columns in the source file that should NOT be mapped, they can be left unmapped (displayed in red). Mandatory fields will require that they be mapped before clicking OK.
Contact Attributes: Select any attributes that should be assigned to ALL contact records in the import file.
Overwrite Duplicates Selecting this box will attempt to match import records to existing records using the contact full name and the organization Custno. Matched records will update the existing record with data from the import file. Blank import file fields will not overwrite, or clear out existing data.
Contact Import File Definitions
f1 - Custno - Adjutant Organization ID for the associated company record
f2 - FirstName - Contact first name
f3 - MiddleName - Contact middle name or initial
f4 - LastName - Contact last name
f5 - Phone1Num - Primary phone number. The import process will attempt to standardize all 10-digit numbers as (###) ###-####.
f6 - Phone1Code - A two-digit code that defines the phone type. The code corresponds with the PHONECODE rule in Adjutant. Typical examples are OF for office, FA for Fax, MO for Mobile, HO for Home. Check your rule setup to be sure of what should be entered here.
f7 - Phone2Num - Second phone number. The import process will attempt to standardize all 10-digit numbers as (###) ###-####.
f8 - Phone2Code - A two-digit code that defines the phone type. The code corresponds with the PHONECODE rule in Adjutant. Typical examples are OF for office, FA for Fax, MO for Mobile, HO for Home. Check your rule setup to be sure of what should be entered here.
f9 - Phone3Num - Third phone number. The import process will attempt to standardize all 10-digit numbers as (###) ###-####.
f10 - Phone3Code - A two-digit code that defines the phone type. The code corresponds with the PHONECODE rule in Adjutant. Typical examples are OF for office, FA for Fax, MO for Mobile, HO for Home. Check your rule setup to be sure of what should be entered here.
f11 - Phone4Num - Fourth phone number. The import process will attempt to standardize all 10-digit numbers as (###) ###-####.
f12 - Phone4Code - A two-digit code that defines the phone type. The code corresponds with the PHONECODE rule in Adjutant. Typical examples are OF for office, FA for Fax, MO for Mobile, HO for Home. Check your rule setup to be sure of what should be entered here.
f13 - Email1 - Primary email address, typically the work address
f14 - Email2 - Secondary email address. This is typically a personal email address or text messaging address.
f15 - Job Title - Contact job title
f16 - Address1a - Business street address (Address1 line)
f17 - Address2a - Business suite or office number (Address2 line)
f18 - Address3a - Business additional address details (Address3 line)
f19 - Citya - Business city
f20 - Statea - Business two-character postal code
f21 - Countrya - Business country code
f22 - Address1b - Home street address (Address1 line)
f23 - Address2b - Home suite or apartment number (Address2 line)
f24 - Address3b - Home additional address details (Address3 line)
f25 - Cityb - Home city
f26 - Stateb - Home two-character postal code
f27 - ZipCodeb - Home zip code
f28 - Countryb - Home country code
f29 - Salutation - Contact salutation, such as Mr., Mrs., or Dr.
f30 - ZipCodea - Business zip code
f31 - DefCont - Enter a 'Y' in this column to check the 'Default Contact' field. This will not update the contact name on the organization screen.
Contact Import Reconciliation
Reconciling imported data should begin with spot-checking several records field-by-field for complete data import. Pick records from the source file that have the most data columns filled in. Verify that all source file data fields imported correctly and display as expected.
Verify that all phone numbers and phone codes imported as expected. Spot-check several phone1 through phone4 records.
Verify that all records have the expected attributes assigned and that the attribute screens load as expected.
Manually update any attributes as needed.
Contact Import Additional Steps
There are no additional steps needed to complete the Contact import.
Contact Import Database Tables
Importing contact records can affect the following databases:
VCONTACT - Each imported user is assigned a unique CONTID value. This is the keyno. Each CONTID is linked to a CUSTID, which matches the ENTID keyno from the ENT table.
USERID - Nothing gets automatically created in this table from the contact import, but if you edit and save the User in Adjutant screen, it will create a table entry.
RTRESOURCE - Similar to USERID, nothing gets automatically created in this table unless you edit and save the Resource screen.
PCXREF - Each attribute record will also create an entry in this table. The PTABLE value for all of these should be CONTACT, and the TYPE value should match the attribute name from Text1 of the associated attribute rule. The PARENTID and CHILDID values will correspond to CONTIDs from the VCONTACT table.